Automatic CNC Gasket Cutting Machine
SLCNC CNC gasket cutting machine is a special equipment for cutting sealing materials. It adopts high frequency vibration cutting technology and is suitable for a variety of gasket such as rubber, asbestos, and silicone.
Its core advantage lies in the high frequency reciprocating motion of the vibration knife head (the vibration frequency can reach tens of thousands of times per minute). There is no fire and high temperature during cutting, which avoids the deformation of the material due to heat damage and ensures that the sealing performance is not affected.
Our gasket cutting machine is equipped with a CNC system, supports the import of CAD drawings, and realizes precise cutting of complex shapes. The error can be controlled within 0.1mm, greatly improving the processing efficiency and consistency. It is widely used in the production of automobiles, pipelines, and mechanical seals.
1. Preparation before cutting
a. Material selection
Common gasket materials include rubber, silicone, PTFE, and etc. It is essential to select suitable materials before cutting, considering the performance criteria of the gasket and the intended use scenarios. For example, in high temperature, strong corrosive environments, polytetrafluoroethylene gaskets are more appropriate than rubber gaskets. Generally, rubber materials can meet most needs in industrial sealing situations.
Once the stock material has been selected, it is time to do a complete inspection of the material. Make sure the surface is flat, and inspect for defects, i.e., cracks, bubbles, impurities, etc. If any of these conditions are present, it will affect both the quality of the cut and the performance of the gasket. Also, measure the thickness of the material to check that it meets the design requirements. For rolled materials, it is necessary to flatten them to avoid wrinkles, which would affect the cut in subsequent stages.
![gasket cutting machine gasket cutting machine]()
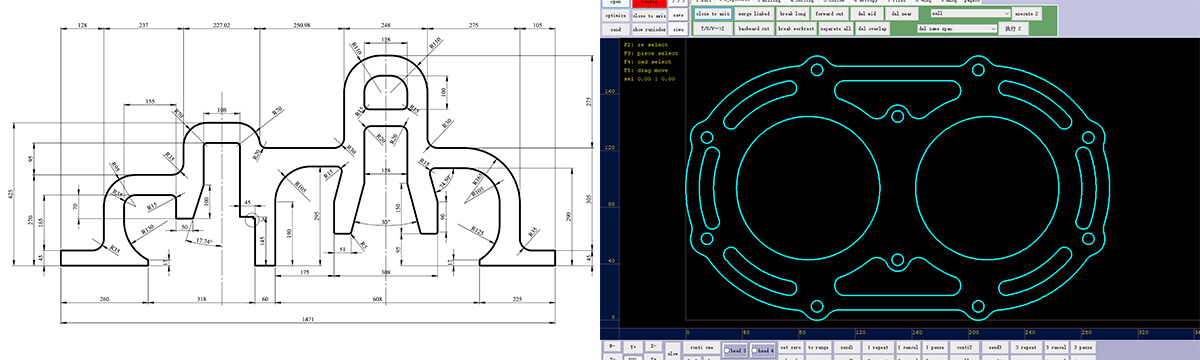
b. Design CAD drawings
![gasket cutting machine gasket cutting machine]()
Use professional CAD software, such as AutoCAD, CorelDRAW, etc., to draw accurate CAD drawings according to the design size and shape of the gasket. During the drawing process, pay attention to the dimensional accuracy of the graphics, and the error should be controlled within a very small range to ensure that the cut gasket meets the use standards. For gaskets with complex shapes, you can import 3D models and perform CAD projection conversion to ensure that the graphics are accurate. After drawing, save the graphics in a file format that our gasket CNC cutting machine can recognize, such as DXF, PLT, etc.
![gasket cutting machine design software gasket cutting machine design software]()
c. Machine inspection
Before starting cutting, check the gasket CNC cutting machine. Clean up the debris on the work surface to prevent these debris from affecting the positioning and cutting accuracy of the material during the cutting process. At the same time, the equipment is not cutting and running, check the various parts of the equipment, including the tool holder, guide rails, transmission devices, etc., to see if there is any looseness, wear, etc. If there is any abnormality, tighten and repair it in time. In addition, check the lubrication system of the equipment to ensure that all moving parts are fully lubricated to ensure the normal operation of the equipment.
2. Gasket cutting machine setting
a. Tool selection
In order to cut gaskets of different materials, thicknesses and hardnesses, our gasket cutting machine can be equipped with electric vibration knives, pneumatic knives, milling cutters and other cutting tools.
![gasket cutting machine cutting tools gasket cutting machine cutting tools]()
Electric vibration knife is used to cut rubber, silicone, etc. with small hardness and thickness | Pneumatic knife is used to cut rubber, silicone with large thickness but small hardness, or PTFE, asbestos, non-asbestos, etc. with large hardness but small thickness. | Milling cutter is used to cut PTFE, asbestos, etc. with relatively large hardness and thickness. |
b. Blade selection
Our gasket cutting machine can cut different thicknesses and shapes. The blade thickness is 0.63mm, 1mm, and 1.5mm. Generally speaking, the thicker the gasket is, the harder it is, and the thicker the blade is.
In addition, in order to cope with graphics of different sizes, the vibrating blade also has different widths. For small-sized arcs, you can choose a blade with a smaller width.
![gasket cutting machine blade gasket cutting machine blade]() | ![gasket cutting machine blades gasket cutting machine blades]() |
| Ordinary blades meet most cutting requirements. | The straight knife blade has a small width, generally about 2.5mm. When cutting small-sized arcs, it can ensure that the shape is standardized and not deformed. However, because the blade width is small, the rigidity is smaller than that of ordinary blades. The cutting speed is slower than that of ordinary blades. The life of the straight knife is shorter than that of ordinary blades. The price of the straight knife is more expensive than that of ordinary blades. |
c. Install cutting tools
Choose a suitable vibrating knife tool according to the characteristics and thickness of the gasket material. Different materials and thicknesses require different types and specifications of tools. For example, when cutting thicker rubber materials, you need to use tools with higher hardness and sharper blades. When installing the tool, turn off the power of the equipment first to ensure safe operation. According to the requirements of the equipment manual, install the tool correctly on the tool holder and tighten it to ensure that the tool is firmly installed and will not loosen or fall off during the cutting process. After the installation is completed, check whether the tool is installed correctly and whether the tool swings flexibly.
d. Parameters setting
Reasonably determine the cutting parameters depending on the type and thickness of gasket material, primarily the cutting speed. Generally, the harder and thicker the material, the slower the speed should be set. If cutting thinner rubber material, a faster speed could be selected, while for thicker or harder rubber, asbestos, and other materials, a speed should be selected that allows a smooth cut. Once you have set the parameters, do a test cut on a small piece of the material, observe the cut, and adjust the parameters untilthe desired cutting state is achieved.
3. Cutting process
a. Loading material
Put the gasket material on the working table of the CNC gasket cutter machine to ensure that the material is within the working range of the machine. And try to ensure that the material is not skewed.
If the gasket material is small, you can manually turn on the fan to confirm whether it can fix the material on the workbench. If it cannot be fixed, you can cover the surrounding plate to increase the adsorption capacity.
![gasket cutting machine gasket cutting machine]()
b. Import CAD drawings
Import the saved cutting graphics file into the control system of the CNC gasket cutter through the operation interface of the equipment. During the import process, pay attention to check the integrity and accuracy of the graphics to ensure that there is no loss or deformation of the graphics. After the import is completed, check the position and size of the graphics in the control system to ensure that the graphics correspond to the placement of the material, and make appropriate adjustments if necessary.
![gasket cutting machine gasket cutting machine]()
c. Start cutting
When the material is securely in position, the cutting graphics are imported properly, and the cutting parameters have been set appropriately, operate the gasket CNC cutter and begin to cut the gasket. During the cutting procedure, the operator should closely observe the cutting situation, look for sobering signs that the tool's running trajectory is following that of the cutting graphics, that the cutting speed is constant and stable and, that there isn't any abnormal vibration or sound. If any issues arise when cutting including, but not limited to, moving materials or tool wear issues, stop the cutting immediately and rectify the situation. After completing the process, re-check that the parameters and equipment are correct beforehand to ensure that the unit can continue to cut.
![gasket cutting machine gasket cutting machine]()
4. Processing after cutting
a. collect gaskets
When the cutting is completed, wait for the tool to stop completely and move the crossbeam to the rear end of the machine. Remove the cut gasket from the work surface. During the removal process, be careful to avoid damage to the gasket, especially for some gaskets with complex shapes and thin edges, be more careful to prevent tearing, deformation, etc.
b. Quality inspection
Carry out an all-round inspection of the quality of the cut gasket. First check if the size meets the design specification requirements. Use measuring instruments such as calipers and micrometers to measure the key dimensions of the gasket length, width and thickness; check that the dimensional error is within the allowable range. Secondly check if the cut edge of the gasket is neat and whether there are defects, such as burrs and gaps. If it is determined that there are quality problems from the gasket check, analyse the problem to determine the cause. Is it improper cutting parameter settings, tool wear, or the quality of the material itself? Take suitable actions to rectify problems.
c. Machine cleaning
After the cutting work is completed, clean the gasket making machine. Remove the debris and waste left on the work surface, clean the knives, guide rails and other parts, and remove surface stains and cutting residues. At the same time, check the various parts of the equipment. If there are any damaged or severely worn parts, replace them in time. After cleaning the equipment, clean the work site, collect the waste materials by category, and keep the work environment clean.
The above is the detailed process of cutting the sealing gasket with the vibration knife cutter. If you have any questions about a certain step, or want to know more related skills, please feel free to communicate with me.