Top Key 10 Questions for Selecting CNC Gasket Cutting Machine
In the gasket manufacturing field, SLCNC gasket cutting machines have become core equipment replacing traditional die-cutting processes due to their flexibility and high precision. However, most purchasers often struggle to make accurate decisions when selecting models, mainly due to cognitive gaps in equipment characteristics, material adaptability, and alignment with production needs. Combining industry practices and SLCNC technical experience, this article sorts out the 10 core issues that receive the most attention during selection, providing systematic references for purchasers. When choosing a vibration knife cutter for gaskets, it is recommended to prioritize these 10 high-frequency questions to quickly align equipment capabilities with gasket process requirements.
Table of Contents |
1. Cutting Principle 2. Cuttable Materials 3. Cutting Tools 4. Cutting Dimensions 5. Ease of Learning and Operation 6. Equipment Stability and Precision 7. Efficiency 8. Material Utilization Rate 9. Maintenance 10. Support and Services |
1. Cutting Principle
The core working principle of SLCNC gasket cutter machine lies in achieving cutting through the relative motion between a high-frequency, small-amplitude vibrating tool head and the material—this design is well-suited to the flexible and elastic properties of gasket materials.
The process can be broken down into three steps:
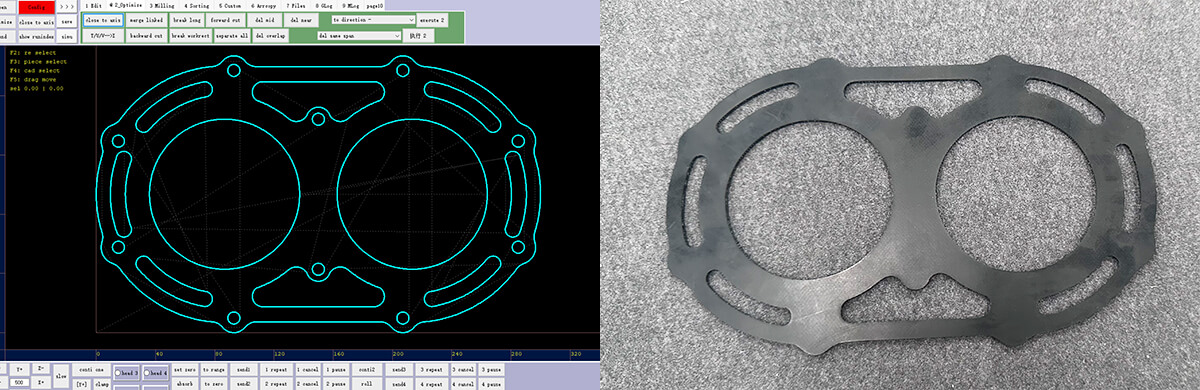
First, the control system receives the gasket graphic file designed in CAD, automatically parses the cutting path, and plans the cutting sequence.
Second, driven by the driving device, the vibration tool head vibrates up and down at a high frequency of tens of thousands of times per minute, creating a motion similar to "high-frequency chiseling" to prevent flexible materials from deforming due to pulling.
Third, the worktable or tool head moves according to the preset path. The high-frequency vibration of the tool head quickly cuts through the material, while a suction device fixes the gasket to ensure the cut edges are free of burrs and collapse, accurately meeting the dimensional precision requirements of gaskets.
![gasket cutting machine gasket cutting machine]()
2. Cuttable Materials
2.1 Rubber
Rubber is the go-to base material for making gaskets, and vibration knives work really well for cutting it. The nice thing about this method is it skips common headaches—like rubber sticking together from high heat, or getting warped because the blade presses too hard. When you’re done cutting, the edges come out smooth, no layers peeling apart or anything.
Breakdown of the rubber types you’ll usually work with:
- Natural rubber: It’s mostly used for sealing jobs where the pressure’s low and the temperature stays pretty normal.
- Synthetic rubber: This is the more versatile bunch. Think nitrile rubber, fluororubber, silicone rubber, and EPDM —each handles different needs, like chemical resistance or high temps.
- Rubber composites: These are rubber mixed with fabric to add strength. Common combos are rubber with nylon cloth or glass fiber cloth—great when you need a gasket that’s sturdier than plain rubber.
2.2 Flexible Polymer Materials
Polyurethane, polyethylene, PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), etc.
2.3 Fibers and Felts
Wool felt, chemical fiber felt, glass fiber cloth, carbon fiber cloth, non-woven fabric, etc.
2.4 Other Special Sealing Materials
Cork, cork rubber, EVA foam, PORON foam, etc.
![CNC gasket cutting machine CNC gasket cutting machine]()
3. Cutting Tools
Regarding the gasket industry, SLCNC automatic gasket cutting machine use primarily "high-frequency vibration knives," as well as pneumatic knives, high-power vibration knives, milling knives and bevel cutters for a diversified mode of processing. The materials processed with these tools includes rubber, silicone, PTFE, graphite, and non-asbestos.
Vibration Knife
Suitable for cutting gasket materials with small thickness and low hardness, such as 5mm rubber, 5mm silicone, and 2mm asbestos.
POT
Suitable for cutting gaskets with medium thickness and hardness, such as 3mm asbestos, 3mm servo materials, and 10mm rubber. Not suitable for low-melting-point silicone; requires an air compressor for support.
400W EOT
Similar cutting capability to pneumatic knives, with slightly higher cutting torque (e.g., for 20mm rubber). No air compressor required.
milling tool
Used for cutting high-hardness gaskets, such as epoxy resin boards, 6mm servo materials, and 6mm asbestos. |
4. Cutting Dimensions
Our CNC gasket cutter has a worktable (usable cutting area) defined as "length x width." The most common worktable sizes are 1600×2500 mm, but small-format worktable sizes (600×400 mm) and large-format (3000×5000 mm) are available. Some manufacturers even have models that can be sized much larger or smaller to fit the width of a coil or limitations of space.
The size of the worktable governs the maximum outer diameter of gaskets that can be cut and will also impact the nesting/lay up efficiency. If you select a model, it may also be necessary to consider the overall measurements of the model and the physical space needed for its installation and operation.
![automatic gasket cutting machine automatic gasket cutting machine]()
5. Ease of Learning and Operation
Our gasket making machine is easy to get started with and simple to operate. After mastering basic CAD design software and parameter settings, new users can usually perform independent cutting within 2 hours. The equipment features high automation, requiring minimal manual intervention during daily cutting.
5.1 Why It’s Easy to Learn
- CNC-driven: Import graphics via computer, and the system automatically generates cutting paths—no complex manual programming required.
- Fixed workflow: Material loading → tool setting → parameter configuration → nesting → cutting → quality inspection; clear and straightforward steps.
- User-friendly interface: Mainstream equipment has a simple human-machine interface, with auxiliary functions such as automatic tool setting, worktable compensation, and nesting.
- Comprehensive training: We provide on-site and remote training to help customers get started quickly.
5.2 Key Points for Learning and Operation
- Master basic CAD design, including graphic creation, import, and path generation.
- Familiarize yourself with material parameters (speed, frequency) and tool compatibility.
- Make good use of functions like tool setting, worktable compensation, and nesting to reduce debugging costs.
5.3 Potentially "Challenging" Links
- First-piece parameter debugging (speed/frequency must match material and thickness).
- Nesting and over-cutting compensation strategies for complex irregular parts.
- Equipment maintenance and tool life management during long-term production.
5.4 Tips for Quick Mastery
- Participate in our hands-on training, which covers tool setting, parameter configuration, nesting, and safety operations.
- Test 3–5 parameter groups using small samples of the same material and record the optimal combination.
- Enable automatic tool setting and worktable compensation to reduce human error.
- Establish weekly inspection and tool replacement checklists to ensure consistent performance.
6. Equipment Stability and Precision
SLCNC gasket CNC cutter maintain stable long-term consistency in structure and control systems, characterized by smooth edges, minimal dimensional deviation, and low batch-to-batch fluctuation. This reliability depends on the systematic coordination of mechanical structure, high-frequency vibration cutting technology, worktable suction, parameter matching, and preventive maintenance.
Key measures taken by SLCNC to ensure machine stability include:
1. Mechanical stiffness: Using heavy-duty frames constructed from welded steel tube, Taiwan Jingyan linear guides and racks and Japanese high-inertia servo motors and drive, allows less vibration at high-speed motion, stabilizes motion trajectory and improves cutting accuracy.
2. High-frequency vibration technology: Using high-frequency vibration knives as cutting tools to reduce cutting resistance, enhance cutting precision, and improve cutting quality.
3. Suction worktable: A vacuum suction system firmly fixes materials to prevent displacement during cutting. Zoned vacuum worktables enhance suction in local areas.
4. Control system: Equipped with Japanese servo motors and drives, the worktable features flatness compensation. Combined with an intelligent control system, this ensures cutting precision.
![cnc gasket cutter machine cnc gasket cutter machine]()
7. Efficiency
The cutting speed of SLCNC gasket making machine is mainly influenced by three core factors:
1. Material properties: Gaskets with high hardness, strong toughness, or large thickness require reduced speed to avoid incomplete cutting or edge chipping. Soft, thin, and easy-to-cut materials allow for higher speeds.
2. Equipment performance: Higher tool head power and vibration frequency result in stronger cutting impact and a higher speed limit. Sufficient torque from servo motors and strong worktable suction support high-speed cutting without jamming or displacement.
3. Cutting requirements: Complex irregular gaskets require frequent corner turns, so their cutting speed is lower than that of regular-shaped gaskets. High-precision requirements also limit speed to ensure dimensional accuracy.
8. Material Utilization Rate
The core ways for our flatbed digital cutter to improve material utilization rate are "intelligent nesting + process and equipment optimization." Through measures such as nesting, common-edge cutting, leftover reuse, suction and parameter matching, and tool strategies, material utilization can usually be increased by approximately 10%–20% compared to manual nesting (reaching over 20% in some scenarios).
- Automatic nesting software has far superior computing capabilities to manual operations, enabling optimized nesting to reduce material waste.
- The CNC system precisely controls cutting positions, eliminating the need for large gaps between cut pieces.
- Automated cutting ensures gasket consistency, reducing defect rates and scrap rates.
![gasket making machine gasket making machine]()
9. Maintenance
The maintenance of SLCNC oscillating knife cutting machine is based on daily and regular maintenance. The primary objective of the maintenance is to keep the tool head stable and the transmission and suction systems stable.
Daily Maintenance (Before Startup Each Day)
- Inspect the tool head blade to see if it has any chips or become loose; clean all debris from the tool holder with compressed air.
- Wipe the suction worktable and clean the suction filter to minimize blockage.
- Check whether the emergency stop button and light curtain/safety switch are functioning correctly,
Regular Maintenance (Weekly/Monthly)
- Wipe the guides and lead screws and applicate the special guide oil and lithium-based grease.
- Clean the suction air duct, check the vacuum pump oil level and/or fan dust.
- After the power off, check all of the wire connections in the electrical cabinet and blow the dust inside the electrical cabinet.
In-depth Maintenance (Recommended Every 6–12 Months)
- Overhaul the tool head bearings and calibrate the tool head perpendicularity.
- Use instruments to calibrate transmission precision and replace aging electrical components. These steps extend overall equipment life and stabilize precision.
(Maintenance Process Photos)
10. Support and Services
As a manufacturer of digital cutting machines, we provide systematic services covering the entire "pre-sales → after-sales → value-added" cycle. These services not only address core needs in equipment procurement and use but also empower customers’ long-term production. Specific service contents are as follows:
10.1 Pre-sales
- Customized cutting solutions: Based on the customer’s gasket material, thickness, precision requirements, production capacity, as well as site size and voltage, we recommend suitable models. We also provide small-batch samples for customer reference to ensure the equipment meets production needs.
10.2 After-sales
- Installation and training: We provide complete installation manuals, operation manuals, and detailed video tutorials. Customers can visit our factory for free training on machine operation; alternatively, we can send technicians to the customer’s factory for on-site installation and training (customer bears related costs).
- 7x24 technical support: An exclusive after-sales service group is assigned to each customer. Technicians can perform remote troubleshooting via phone or video when equipment breakdowns occur, most issues will be resolved on the same day.
10.3 Value-added Services
- Consumables supply: Provide original compatible consumables to customers at cost price to reduce their operating costs.
- Software upgrades and technical iterations: Offer free function upgrade services for the equipment control system.
- Customer case and experience sharing: Regularly share industry-specific equipment application cases and production optimization tips with customers to help them improve production capacity.
![gasket cutting machine manufacturer gasket cutting machine manufacturer]()
Selecting a gasket vibration knife cutter is essentially a process of matching "production needs, material characteristics, and equipment performance." Purchasers should avoid blindly pursuing "high parameters" and instead start from actual production capacity, product specifications, and industry standards. By combining test cutting and after-sales support, choose equipment that balances "practicality, scalability, and cost-effectiveness."
SLCNC CNC cutters, with their modular design, multi-tool compatibility, and global after-sales support, have become a preferred solution for gasket production in various industries. It is recommended that purchasers clarify their core needs before selection and communicate in depth with our technical team to ensure the equipment can empower production in the long run.